During this time they are learning to classify objects by their physical characteristics such as size and appearance. Seriation is part of the concrete operational stage of development and is closely related to classification.
 Nce Practice Question Nceprep Piaget S Preoperational Stage A Is The Final Stage Which Includes Abstract Reaso Cognitive Development Jean Piaget Cognitive
Nce Practice Question Nceprep Piaget S Preoperational Stage A Is The Final Stage Which Includes Abstract Reaso Cognitive Development Jean Piaget Cognitive
Concrete operational children recognize that certain physical characteristics of objects remain the same even when their outward appearance changes.
/2795457-article-piagets-stages-of-cognitive-development-5a95c43aa9d4f900370bf112.png)
Examples of concrete operational stage in the classroom. Understand conservation and compensation. Concrete operational stage- 7-11 years. Children in this stage should be encouraged to work in groups in school to explain and discuss hypothetical topics.
Use visual aids andor props when teaching complex or abstract ideas. I know there has to be ten she said to herself because thats how many I put in that little pile on my desk yesterday. As a teacher this stage has implications for how to convey information so that children have adequate comprehension.
They are also learning to make inferences but still have difficulty with deductive reasoning. In Piagets Three-Mountain Task for example children in the concrete operational stage can describe how a mountain scene would look to an observer seated opposite them. Imitation memory and thought begin to be utilized.
Able to solve hands-on problems logically. 35 summarized this stage as. In both instances the person is using an organizational schema or system to make.
By presenting a concept with a graphic or some form of visual aid students will have a concrete object to. Language development and recognizing symbolic form. An example of the distinction between concrete and formal operational stages is the answer to the question If Kelly is taller than Ali and Ali is taller than Jo who is tallest This is an example of inferential reasoning which is the ability to think about things which the child has not actually experienced and to draw conclusions from its thinking.
Understand that the physical world is stable identity Solve hands-on problems logically. During the third stage the concrete operational stage from ages 7 to 11 the child begins to conceptualize create logical reasoning and use operations such as classifying and ordering. In the concrete operational stage for example a child may unconsciously follow the rule.
After spilling 10 pennies stacked on her desk Lizzie bent down to search for them. Sensorimotor stage 0-2 years. Have then discuss social issues in groups and brainstorm.
Able to think backward from end to. Children can order fractions using different measuring utensils to. Here are some strategies that can be used to best allow students to learn and understand concepts.
Another important cognitive ability is what Piaget termed conservation. They can represent operations in their minds and solve problems for items or situations that are far removed from their physical space. Able to solve abstract problems in a logical fashion.
In the concrete stage students still rely on concrete materials and situations they have already experienced when interpreting new information. Have them write a short story on a hypothetical topic such as what life would be like in outer space. In the fourth stage the formal operational stage from ages 11 to 16.
Formal operational stage- 11-15 years. Children in the formal operational stage differ because they are able to perform abstract thinking. Late elementary to middle school years.
This allows the child to apply their new creative aspect. For example children in the concrete operational stage are just beginning to form rudimentary logic. During this stage which begins around age seven and lasts until age 11 children begin to implement operational thought.
Anita Woolfolk 2010 p. Preoperational stage- 2-7 years. If nothing is added or taken away then the amount of something stays the same This simple principle helps children to understand certain arithmetic tasks such as in adding or subtracting zero from a number as well as to do certain classroom science experiments such as ones involving judgments of the amounts of liquids when mixed.
In other words kids are not only able to start thinking about how other people view and experience the world they even start to use this type of information when making decisions or solving problems. Piaget called this period the concrete operational stage. Using real-life examples helps students relate topics to prior knowledge.
For example introducing fractions can include relating them to measurements used in a chocolate chip cookie recipe. This is the ability to understand that an object.
 Examples Of Concrete Operational Activities Page 1 Line 17qq Com
Examples Of Concrete Operational Activities Page 1 Line 17qq Com
 Concrete Operational Stage Simply Psychology
Concrete Operational Stage Simply Psychology
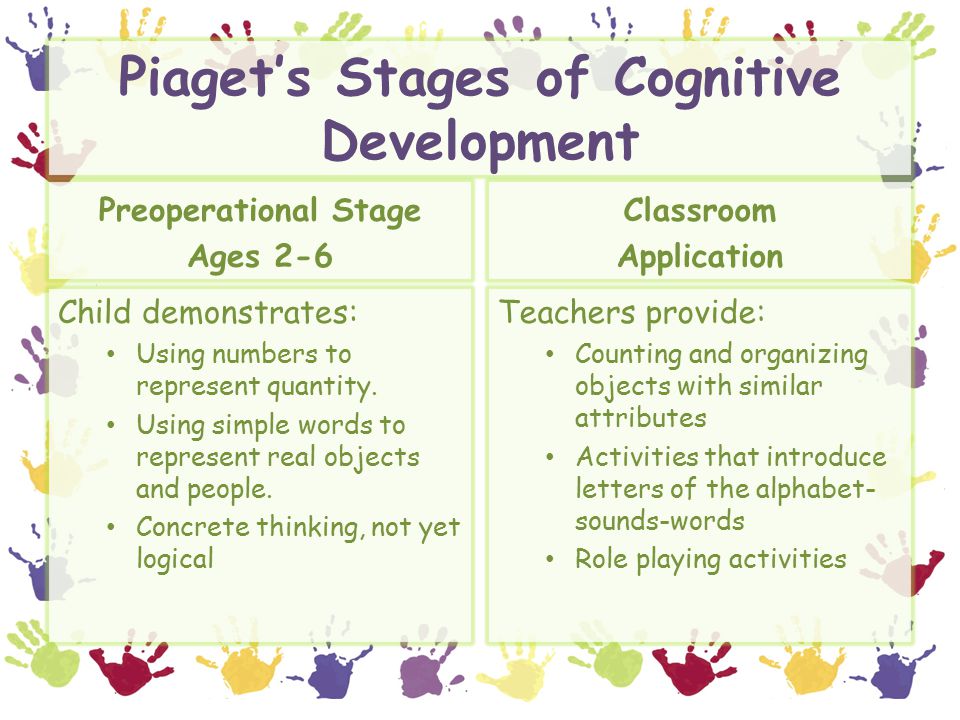 Buy Piaget Concrete Operational Stage Activities Up To 72 Off
Buy Piaget Concrete Operational Stage Activities Up To 72 Off
 Adolescence Cognitive This Is A Great Diagram That Goes In A Little More Detail Of Piaget S Fourth Stage For Cognitive Development Metacognition Adolescence
Adolescence Cognitive This Is A Great Diagram That Goes In A Little More Detail Of Piaget S Fourth Stage For Cognitive Development Metacognition Adolescence
 Piaget Concrete Operational Page 1 Line 17qq Com
Piaget Concrete Operational Page 1 Line 17qq Com
 Solved The Concrete Operational Stage Years During This Chegg Com
Solved The Concrete Operational Stage Years During This Chegg Com
/formal-operational-stage-of-cognitive-development-2795459-5bad1e3a46e0fb0026179d94.png) Formal Operational Stage Of Cognitive Development Explained
Formal Operational Stage Of Cognitive Development Explained
 Concrete Operational Stage Definition Examples Activities More
Concrete Operational Stage Definition Examples Activities More
 Ormrod Explains That During Piaget S Concrete Operational Stage Ages 6 12 Chil Cognitive Development Activities Piaget Stages Of Development Learning Theory
Ormrod Explains That During Piaget S Concrete Operational Stage Ages 6 12 Chil Cognitive Development Activities Piaget Stages Of Development Learning Theory
 Piaget S Formal Operational Stage Definition Examples Psychology Class 2021 Video Study Com
Piaget S Formal Operational Stage Definition Examples Psychology Class 2021 Video Study Com
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/concrete-operational-stage-of-cognitive-development-2795458-5b92b8e646e0fb0050c8df61.png) Concrete Operational Stage Of Cognitive Development Explained
Concrete Operational Stage Of Cognitive Development Explained
/2795457-article-piagets-stages-of-cognitive-development-5a95c43aa9d4f900370bf112.png) Piaget S 4 Stages Of Cognitive Development Explained
Piaget S 4 Stages Of Cognitive Development Explained
 Concrete Operational Examples Page 1 Line 17qq Com
Concrete Operational Examples Page 1 Line 17qq Com
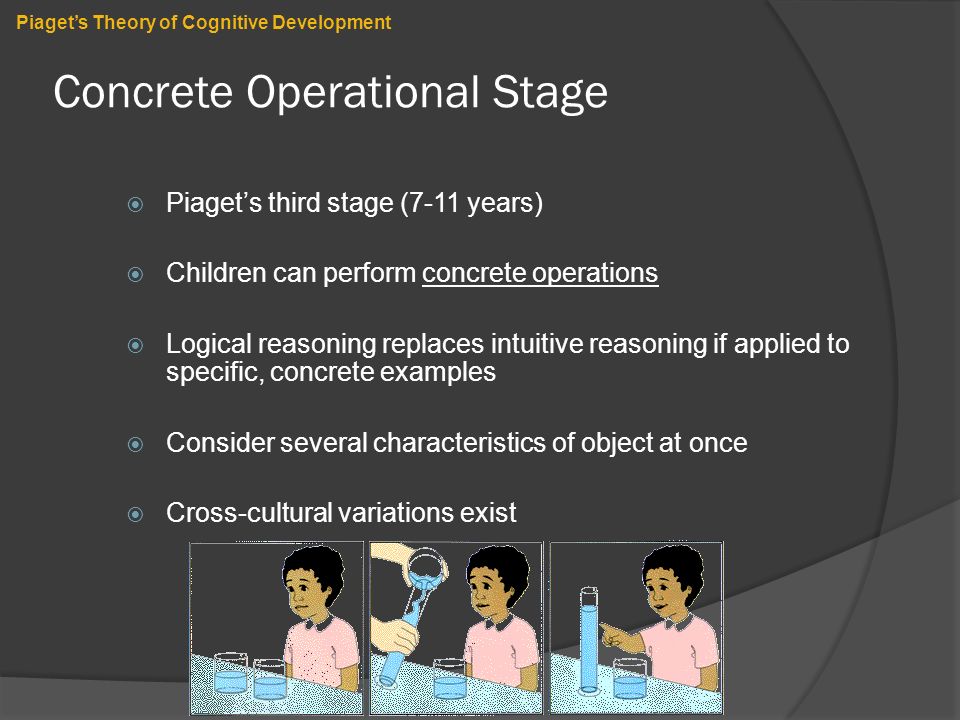 Cognitive Approaches Piaget S Theory Of Cognitive Development Ppt Video Online Download
Cognitive Approaches Piaget S Theory Of Cognitive Development Ppt Video Online Download
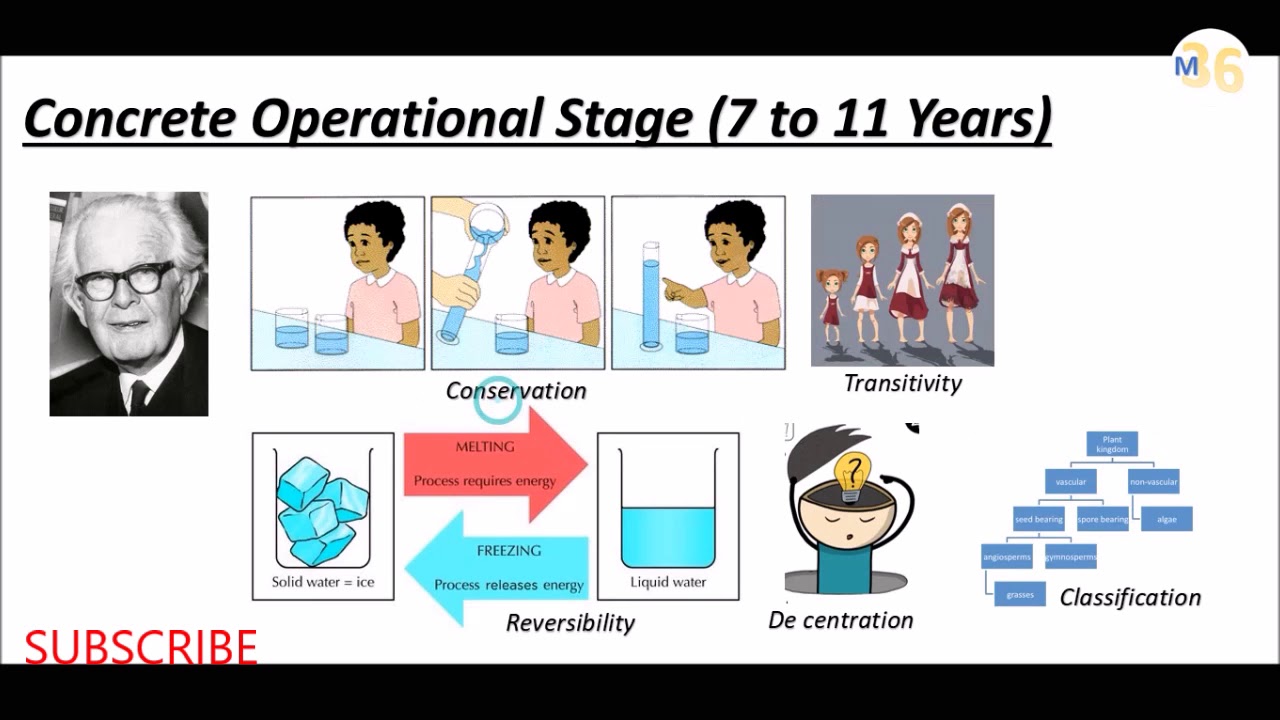 Concrete Operational Stage By Mentors 36 Kvs Dsssb Ctet D Ed Youtube
Concrete Operational Stage By Mentors 36 Kvs Dsssb Ctet D Ed Youtube



